

It holds within it an incredible wealth of knowledge that astronomers have been teasing out for the past few decades. The primordial cosmic microwave background (CMB) radiation has since traveled some 13.8 billion years through the expanding cosmos to our telescopes on Earth and above it.īut the CMB isn’t just light. This light is the remnant signature of the cosmic beginning - a dense, hot fireball that burst forth and created all mass, energy, and time. X-ray characteristics pointing to huge amounts of material falling into supermassive black holes in very distant galaxies (Fig 3).A glow undetectable to the human eye permeates the universe. Some of this enigmatic background into many faint individual sources, their In 2000, however, more powerful orbiting X-ray instruments, such as the XMM-Newton Observatory, have resolved First revealed in the 1970s byĮarly X-ray satellites, its origin proved something of a mystery. The cosmic X-ray background (CXB) is an X-ray and gamma-ray glow that comes from all parts of the sky. Present, pulling gas together shortly after the Universe's birth, and enabling Idea that a great deal of dark matter was The brightness indicates that there was an incredibleīurst of star formation during the Universe's youth. That the CIB is two to three times brighter than expected based on extrapolations Measurements of the CIB by the 2MASS telescope, published in 2002, confirmed The history of galaxy formation, and the presence or absence of dust in The intensity and spectrum of the CIB provides information The cosmic infrared background (CIB) is the total of the redshifted and reprocessed radiation from the era of galaxyįormation.
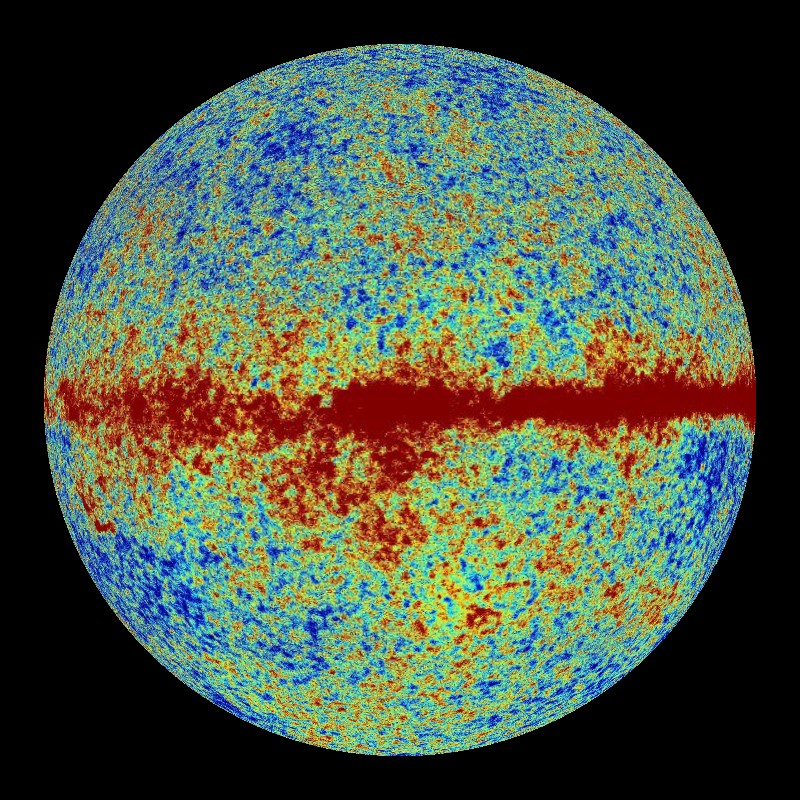
Have been critical to the formation of the first galaxies (Fig 1). In temperature of the CMB with direction these are taken to indicate slightįluctuations in the density of matter in the early universe, which would Sensitive measurements of the microwave background by the Cosmicīackground Explorer (COBE) and other spacecraft have shown slight variations So that it now appears as if it has come from a blackbody with a temperature of just 2.73 K. Into the microwave region of the spectrum The temperature of the universe at that time was aboutģ,000 K, but the expansion of the universe has redshifted the relict radiation Was first able to travel freely over great distances without being absorbedīy ordinary matter. The cosmic microwave background is the strongest component of the cosmic background radiation and is believed to have originated in the decoupling era, about 300,000 It had been predicted theoreticallyīut was first observed in 1964 by the American telecommunications engineers The cosmic microwave background (CMB) is diffuse electromagnetic radiation, most intense around a wavelength of 1 Together the infrared-optical backgroundsĪdd up to about 9% of the CMB's intensity. Near-infrared background and optical background combined have a total intensity of slightly The cosmic far-infraredīackground has a total intensity of 34 nW/m 2/sr, while the cosmic Is the solid angle whose opening is one radian). NW/m 2/steradian (nW = nanowatt, or 10 -9 W "steradian" Of theseĬomponents, the CMB is by far the largest, with a total intensity of 996 Infrared background, and cosmic optical background (COB).

The cosmic background radiation is diffuse electromagnetic radiation coming fromĪll parts of the sky.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
